Supporting imagery
Models

Released on 26/04/1990 in Japan and on 01/07/1991 America and Europe
Motherboard
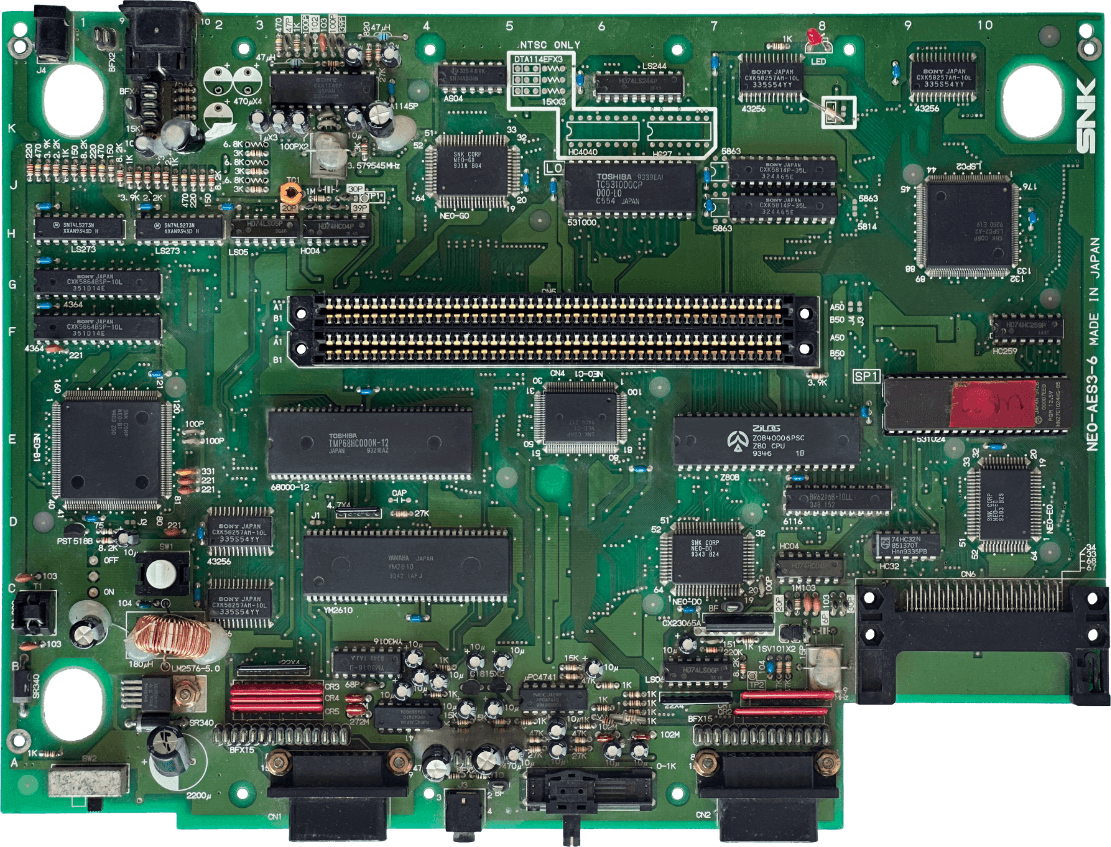
Showing revision 'NEO-AES3-6'.
I took this photo using the model I bought. Also, the previous owner re-arranged some capacitors to improve the video signal.
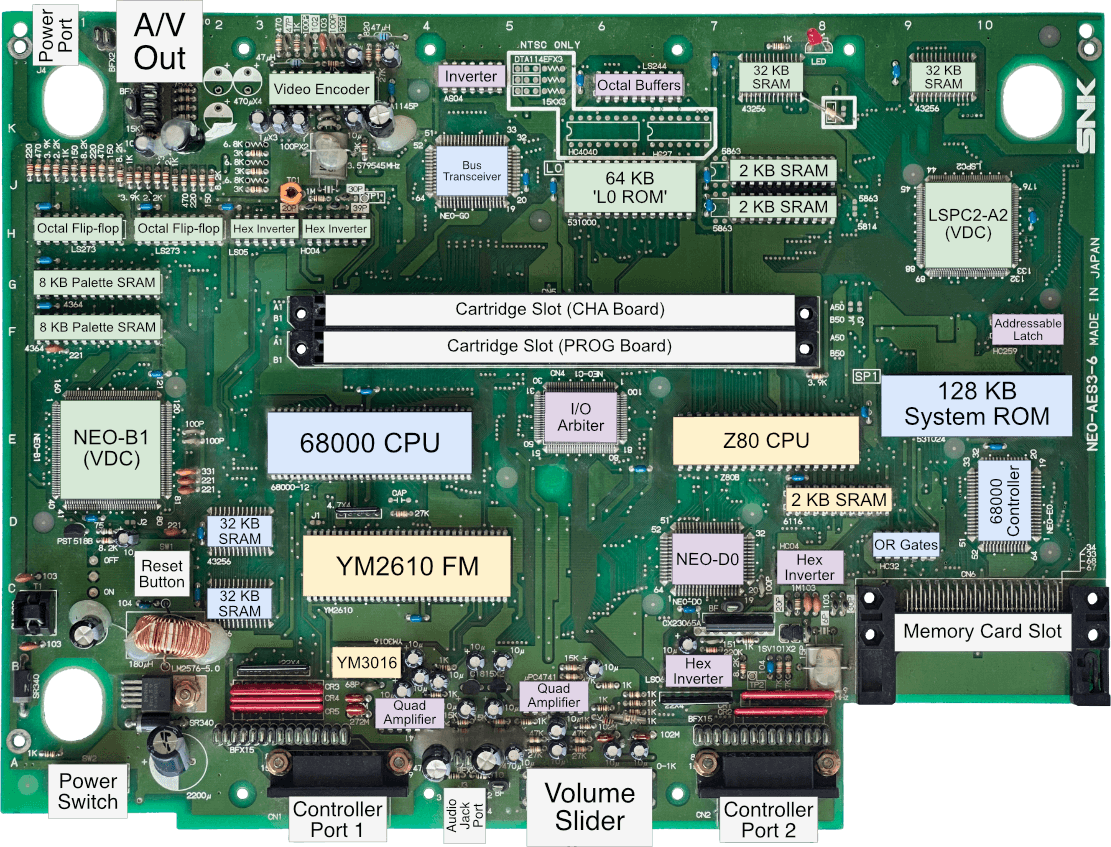
Diagram
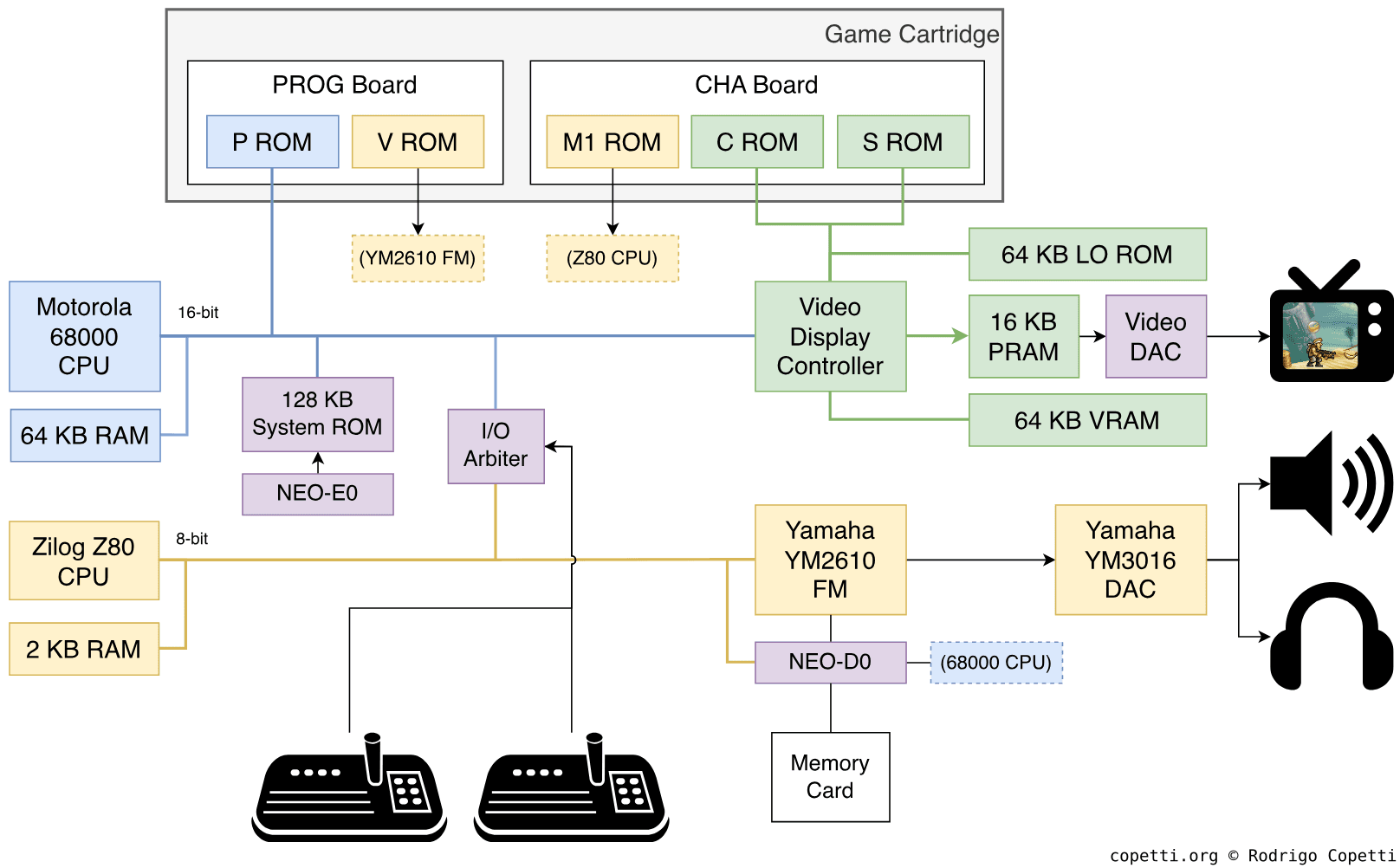
A quick introduction
Straight from the arcade world, the Neo Geo was, without a doubt, the most expensive hardware of the 4th generation. This begs the question: how capable was it and how did it compare to the rest?
In this entry, we’ll take a look at the result of one company (SNK) setting aside budget restrictions and shipping a product meant to please both arcade owners and rich households.
Models and variants
The Neo Geo is exceptional in the sense it was designed for two markets at the same time: the arcade and the home. Consequently, SNK produced a single architecture which was sold in the form of two variants, each catering to a particular market:
- The Multi Video System or ‘MVS’ is the form tailored for arcade centres. Its I/O follows the ‘JAMMA’ specification (with some deviations [1]), facilitating integration with arcade cabinets. Alongside, its specialised motherboard provides extra circuitry for handling coin-based payments. Be as it may, throughout its lifetime, SNK ended up shipping tons of revisions, some of which could accommodate up to six game cartridges at once [2].
- The Advanced Entertainment System or ‘AES’ is the simplified design for homes. While smaller and with reduced I/O, it doesn’t compromise its fundamental capabilities.
I suppose I should also mention the Neo Geo CD, which is the successor to the AES variant and embraced the CD-ROM for game distribution. Just like its previous forms, there were multiple revisions of this model.
In any case, for this analysis, I’ll be focusing on the AES variant, as that’s the one I’ve got with me. I will, nevertheless, make deserved references to the MVS when it comes to bonus functionality.
CPU
The system features a dual-processor configuration consisting of a Motorola 68000 and a Zilog Z80 CPU, two major icons of 80s electronics. The 68000 is tasked with executing the main program (also known as the game) while the Z80 is relegated to sound management [3]. You may recall identical roles in the Mega Drive/Genesis, but that’s where similarities end, as the chip variants and layouts are somewhat divergent.

To give you an example, the Neo Geo’s 68000 runs at 12 MHz (4 MHz faster than the Mega Drive’s). Additionally, the specific chip fitted is the 68HC000, a variant distinguished by its use of CMOS gates (as opposed to the previous and less-efficient NMOS process).
If you want to know what’s inside the 68000 and the Z80, I have done previous analyses in the Mega Drive/Genesis and the Master System articles, respectively. Thus, for the Neo Geo study, I will focus on their new uses.
A multitude of support chips
The most notable difference between the Neo Geo and any home console of the same generation is that, during the design of the former, SNK wasn’t constrained by the budget limitations of the average household. In doing so, the motherboard features an extraordinary number of integrated controllers that not only remove many bottlenecks from the CPUs but also expand their capabilities.
The list of chips is lengthy, but the most confusing aspect is that, throughout revisions, SNK redesigned the chipset, either by unifying multiple chips or splitting them. So, for now, let me tell you that the motherboard contains the following groups of ‘accelerators’:
- 68k Controllers: To seamlessly switch between vector tables. I explain this area in the next paragraphs.
- Z80 Controllers: To alleviate the memory addressing limitations.
- I/O Arbiters: To delegate all I/O operations, saving cycles along the way.
- Video Display Controller: To carry out all graphics operations. This will be discussed in a dedicated section called ‘Graphics’.
- Cabinet controllers: For the arcade variant only (the ‘MVS’). These handle the coin slot, provide a scoreboard, and perform system diagnostics.
- Home controllers: Likewise but only found on the home variant (the ‘AES’). In this group, we find a video encoder that generates TV-compliant video signals.
From now on, I will use these titles to refer to any group throughout the article. In some cases, I will also name specific chips within the groups to denote special importance.
Sophisticated I/O handling
Let me introduce you to a noble capability of the 68000 which I have not covered until now: the vectorised interrupt table. Earlier CPUs like the 6502 and the Z80 had a constrained design for handling I/O communication. Whenever an external device wanted the attention of the CPU, the former had to send an interrupt request which, in turn, required the CPU to run a software routine to process it. The amount of information provided during the request was very limited, meaning the CPU needed to spend extra cycles to investigate ‘who’ triggered the interrupt and ‘why’ the CPU was interrupted.
To be fair, CPUs like the Z80 provided extra circuitry to allow the peripheral to tell the CPU which instruction to execute next. Nevertheless, this wasn’t widely adopted.
The 68000 improved this technique by treating interrupts as exceptions. Peripherals are required to identify themselves when they interrupt the CPU [4]. The latter then uses the identifier to compose a memory address, which in turn points to a tailored software routine. All in all, this enables programmers to handle I/O communication efficiently, as they can now catalogue their dedicated interrupt handlers in a memory area called autovector table, and the CPU will execute each automatically.
The Neo Geo takes advantage of this design with the addition of a controller chip called the NEO-E0. Essentially, both the Neo Geo’s Operating System and the game implement a dedicated exception table; this is because the OS table focuses on hardware interfacing and the game table is used during normal execution. However, the 68000 is only aware of one at a time. So, the NEO-E0 provides automatic bank switching that ensures the 68000 reads from the right table at all times.
Inter-process communication
Whenever a system features a dual-processor layout, there must be a way for both CPUs to communicate. In this console, SNK implemented inter-process communication (IPC) through the use of an I/O arbiter chip. The latter exposes a single 8-bit register, which the 68000 can write to [5].
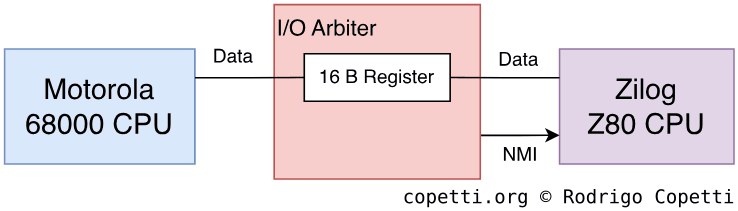
Once the register is updated, the arbiter will send a non-maskable interrupt to the Z80. From then on, the Z80 may read the value (mapped to a port) and react accordingly. This includes writing back to that register, so the 68000 receives new data. However, for some reason, the 68000 is not interrupted (so it needs to perform some sort of polling).
The specific I/O arbiter chip has changed across different motherboard revisions. It was first implemented with the ‘PRO-B0’ chip and later replaced with the ‘NEO-C1’.
Anti-unpleasantries
Speaking of interruptions, something that arcade cabinets cannot afford is requiring constant maintenance.
We are no strangers to games suddenly freezing due to a software bug. The fix is no mystery either: just power cycle and start the game again. Now, imagine if this were to happen to an arcade cabinet. Unless the owner happened to be nearby, the broken cabinet would only be losing money.
The Neo Geo - having inherited the requirements of coin-slot machines - provides an ‘auto-repair’ process by bundling a Watchdog program. This is found in the I/O arbiter chip [6].

The system works as follows: games are required to periodically notify the watchdog of their presence (by writing to a particular register). In the unfortunate event that the watchdog does not receive a ping after a certain period, it will assume the program has frozen and proceed to reset the system.
Thanks to this, MVS owners did not need to keep an eye on their cabinets. Meanwhile, those lucky kids who could afford an AES system did not even have to move from their luxury sofas whenever their games crashed.
If that weren’t enough, MVS motherboards complement this system by fitting an extra microcontroller, the NEO-F0. This drives the coin lockout mechanism, preventing users from wasting coins on failed systems [7], among other things.
Memory available
Memory is scattered across the motherboard and the game cartridge (which, by the way, is massive in size). Remember this is an expensive system, so memory bandwidth and capacity were top priorities.
In the case of general-purpose memory, there are 64 KB of RAM available to the 68000. Meanwhile, the Z80 is provided with 2 KB.
MVS models additionally include another 64 KB. This is battery-backed and intended to store game scores, so it is not available for general purposes, however.
Curiously enough, this system does not feature any form of Direct Memory Access (DMA) to speed up memory transfers. I presume it is not a requirement, considering the number of dedicated buses.
Graphics
The Neo Geo is the pinnacle of tile-based graphics, its richness of colours is comparable to frame-buffer-based systems (which only became affordable four years later). Be as it may, when it comes to effects, the Super Nintendo has managed to do more with less.
Design
The graphics subsystem revolves around the typical Video Display Controller (VDC) model, but this time it is surrounded by a considerable number of components. The result is a console that can display tons of sprites - so many, in fact, that the iconic background layers are no longer relevant. This makes sense, as backgrounds were originally devised to tackle the limited number of sprites.





That being said, the console broadcasts a frame compliant with NTSC and PAL signals (the choice depends on the region). In this case, they carry a dimension of 320 x 224 pixels (for NTSC) or 320 x 256 pixels (for PAL) [8].
The chipset
The group of chips in charge of drawing to the TV has evolved as new revisions were released. Over the years, SNK alternated between NEC and Fujitsu to manufacture their integrated circuits.


For explanatory purposes, let us start by describing the most notable chips in the set:
- The Motorola 68000. You already know it as the main CPU. Its main role is to fill the VRAM and Palette RAM; and set up the VDC (using a set of exposed registers).
- The Video Display Processor (VDC): Based on the information stored in multiple memory chips, it generates scan lines and sends them to ‘Palette RAM’, which will, in turn, generate the required colour pixels.
- The physical appearance of the VDC will vary depending on the motherboard model. For instance, the first revision housed three chips (the ‘LSPC-A0’, ‘NEO-B0’ and ‘NEO-C0’), whereas later ones use a combination of the ‘LSPC-A2’ and the ‘NEO-B1’.
- The Video DAC: Converts the colour stream received from ‘Palette RAM’ into a video signal.
Don’t worry if the previous explanation is too dense. All of this will be explained more calmly in the following sections. Now, let’s move on to analysing the information these chips operate on.
Organising the content
Graphics data is distributed across two separate boards. The first is the console’s motherboard, and the other is found in the game cartridge. You may recall a similar arrangement implemented in the NES/Famicom.
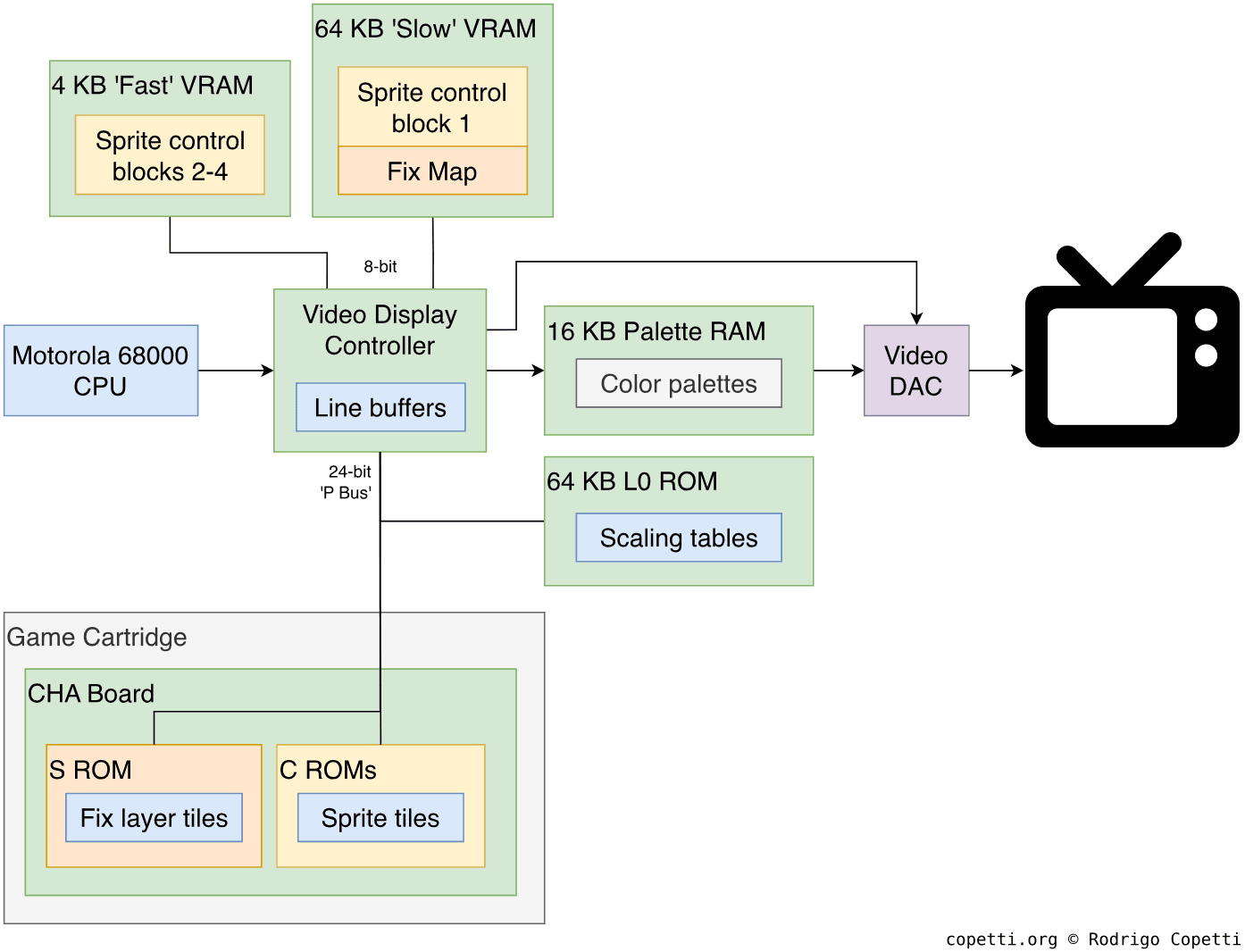
On the motherboard, we find:
- 68 KB of VRAM: Stores sprite attributes and tile references.
- Physically, VRAM is divided into 4 KB of ‘Fast’ VRAM and 64 KB of ‘Slow’ VRAM. Each is connected via a dedicated bus and exhibits drastically different latency. This conditions the number of cycles the CPU must wait after updating its content.
- Four line buffers: Store the scan lines rendered by the VDC. They only encode tile data that must be combined with other data in Palette RAM.
- 16 KB of Palette RAM: Stores the palettes of colours used by the graphics. This block is also tasked with sending pixel colours to the Video DAC.
- 64 KB of ‘L0 ROM’: It so happens the VDC can shrink sprites. To achieve this, the ‘L0 ROM’ stores lookup tables that tell the VDC which scan lines to render based on the zoom value requested. [9].
The corresponding board in the game cartridge is referred to as CHA Board and fits the following:
- Multiple C ROM chips: Store tiles for the Sprite Layer.
- An S ROM: Stores tiles for the ‘Fix’ Layer (I explain this layer in the next section).
Constructing the frame
Now that you’ve had a glance at the most important components, let me give you a quick summary of how the graphics subsystem turns data into an image - in other words, how it renders a frame:
- The CPU fills VRAM with the required references for the sprite layer and Fix layer.
- Based on the information in VRAM, the VDC fetches graphics from C ROMs and the S ROM, and stores them in the line buffers.
- While fetching occurs, the VDC uses the information in the line buffers to latch Palette RAM. This causes the latter to send colour pixel data to the Video DAC.
- The Video DAC outputs a video signal to the TV.
Based on these steps, let me provide a thorough explanation using Art of Fighting 3 as an example.
Tiles


Traditionally known as 8 x 8 pixel bitmaps, tiles are the primary ingredient to build the graphics of the 4th generation. Due to its unique attributes, the Neo Geo only draws two types of graphics: fix tiles and sprites. Thus, tiles are encoded and stored separately depending on the graphic type. In both cases, each pixel is encoded using 4 bits (in other words, 4 bpp), meaning it can select up to 15 colours plus transparency.
In terms of colour composition, Palette RAM allows storing 256 colour palettes [10]. Each palette is made of sixteen colours referencing 16-bit RGB values. Among all the available slots, there are two reserved entries: the ‘Reference colour’, which must be hardcoded to $8000 (pure black); and the ‘Backdrop colour’ which encodes an arbitrary colour that is displayed in the absence of tiles.
The CPU may update Palette RAM at any moment, but it should only do so during blanking periods. Otherwise, a snowing effect will appear.
Fixed plane

The Fixed plane is a layer 320 x 256 pixels (40 x 32 tiles) wide [11], pretty much the entire screen. Its tiles displayed are completely static and only have access to 16 colour palettes. In practice, this is used to display ‘always-on’ information, similar to the window layer of the Game Boy.
When broadcasted to a CRT screen, the displayed area will be smaller. Thus, its safe area is 38 x 28 tiles wide.
Fixed tiles are declared in a region of VRAM called Fix map. It takes the form of a 40 x 32 table, and each entry corresponds to a position on the screen.
The S ROM stores the exclusive tiles for the fixed plane in the cartridge. The VDC can only address up to 128 KB, but this limitation can be extended by bundling a mapper [12].
Sprites

As you may know, sprites are freely moving tiles. Yet, in the case of the Neo Geo, the tiles used for sprites are exceptionally 16 x 16 pixels wide. With that in mind, the VDC can compose sprites ranging from 16 x 16 pixels (1 x 1 tiles) to 16 x 512 pixels (1 x 32 tiles). The reason for providing such tall compositions is that any sprite can also be combined horizontally by ‘attaching’ them to the previous one (though they still count as separate sprites). Overall, there is a limit of 96 sprites per scan line and 381 per frame [13], a large number compared to its competitors.
In terms of effects, sprites can be flipped and/or shrunk. These attributes are stored in the ‘fast’ block of VRAM, allowing the CPU to update them without considerable latency.
Due to their complexity, sprites are encoded in four areas in VRAM called Sprite Control Blocks (SCB), each of which stores the following attributes [14]:
- SCB1: Tile reference, colour palette reference, and X/Y flip.
- SCB2: Horizontal and vertical shrink.
- SCB3: Y position, vertical size (in terms of tiles) and whether the sprite is attached to the previous one.
- Sprite attachment causes the second sprite to inherit the predecessor’s attributes, except for the horizontal shrink.
- SCB4: X position.
As you can see, for practical reasons, the last three blocks are stored in fast VRAM, while the first is stored in slow VRAM [15].
Result
While competitors are known for rendering at the pace of the CRT beam, the Neo Geo implements a line buffer rendering system. With this approach, the console stores the rendered scan lines in the aforementioned buffer, rather than beaming them directly to the screen. Since the VDC incorporates enough memory for two scan lines, this allows the VDC to render one scan line while displaying the other, thereby enabling games to update graphics during active display (aside from H-Blank and V-Blank).
Truth be told, the VDC will still be accessing VRAM at the same time, so the CPU must wait between 12 and 16 cycles [16] (depending on the operation) before accessing VRAM again; otherwise, the next operation will be ignored (hence the use of two VRAM variants).
Broadcasting the frame
To broadcast the rendered scan lines, the process varies depending on the console variant (AES or MVS).
The home model adds a video encoder to generate the composite and RGB signals. The A/V connector is somewhat similar to that of the Master System and MegaDrive, but is not interchangeable.
There is nothing of the sort in the MVS model, as the JAMMA protocol leaves that task to the cabinet’s monitor. Thus, the motherboard sends a raw RGB plus sync signal.
Audio
Remember the Z80 CPU I mentioned at the start of the article? It is still the typical 4 MHz CPU you have seen in many other consoles and microcomputers, but now it’s got the privilege of driving a very versatile sound chip: the Yamaha YM2610.

The YM2610 is another FM synthesiser from the popular Japanese manufacturer. It is closely related to the YM2612 featured in the Mega Drive, but do not let its name fool you, as the Neo Geo version is a bit more premium (albeit with some compromises).
Both the YM2610 and YM2612 are part of the high-end ‘OPN’ series, meaning Yamaha enables four operators per FM channel. Now, the Neo Geo’s chip features four FM channels, which, to be fair, is two fewer than the YM2612. That is as far as the weaknesses go.
The FM channels are provided with a Low-Frequency Oscillator (LFO) to modulate either the amplitude or frequency of the operators. The LFO contains a predefined set of frequencies ranging from 3.98 Hz to 72.2 Hz [17].
Now, even though the YM2610 is known for its FM synthesis, it houses additional functions that did not go unnoticed by music composers [18]:
- A Software-controlled Sound Generator (SSG): This is Yamaha’s name for a Programmable Sound Generator (PSG). In essence, the chip bundles a legacy Yamaha YM2149 inside, this can generate three square waves with optional noise. It also comes with an envelope control.
- The original YM2149 came with an interface called ‘I/O ports’ to transfer data between the CPU and another component [19]. Since this is now irrelevant, the embedded variant in the YM2610 doesn’t include it.
- Seven ADPCM channels: Enables to play samples using the 4-bit ADPCM format. These channels are split into two groups:
- ADPCM-A: Consists of six channels, providing a sample resolution of 12 bits and a sampling frequency of ~18.5 kHz.
- ADPCM-B: This is the remaining channel, with a 16-bit resolution and a sampling frequency of up to ~55.56 kHz (better than CD quality).
The YM2610 is connected to two memory chips in the cartridge called V ROMs. These store the ADPCM samples, with one V ROM per ADPCM group.
All in all, the audio subsystem is a combination of the 3rd, 4th, and (then unreleased) 5th generation of consoles. However, unlike the CD medium, Neo Geo cartridges can only store so much, so the ADPCM channels are mainly bottlenecked by storage limitations. In any case, some games found clever arrangements for ADPCM while leaving FM as a secondary constituent [20].
Finally, the YM2610 is paired with another chip to work: the Yamaha YM3016. The latter is a dedicated 16-bit Digital-to-Analogue Converter (DAC), which takes the digital signal output from the YM2610 and converts it to analogue audio (that speakers understand).
The conductor
For the audio chip to do anything meaningful, the Z80 must command it properly. So, the Z80 runs a program stored in yet another distinct chip called M1 ROM. This is found inside the game cartridge, particularly, within the CHA Board. The program for the Z80 is often referred to as the sound driver, and there were many implementations [21].

On a similar note, the Z80 is paired with a proprietary controller called NEO-D0; the latter acts as a memory bank and I/O controller.
Operating system
There is a 128 KB ‘System’ ROM found on the motherboard [22]; this serves as the typical BIOS, providing:
- A bootloader to initialise the hardware, perform a self-test, and bootstrap the splash animation.
- A configuration shell (only on MVS models).
- Various system routines that abstract hardware operations.
The visual services
After powering on the console, the user will notice a splash screen known as the Eyecatcher [23]. Its code is stored in the System ROM, but the graphic assets (the Neo Geo logo and other labels) are fetched from the cartridge’s C ROM and S ROM.
Alternatively, the P ROM header may contain a flag instructing the System ROM to delegate the splash routine to the cartridge [24]. This only works on the AES variant [25], yet later games adopted this to display different text.


The MVS system also provides a Test Menu to configure the cabinet (e.g., adjust the calendar, test the components, etc.). This menu is triggered by flipping one of the DIP switches of the MVS (inaccessible to the end user). Consequently, its motherboard bundles an S ROM that stores the Fix tiles for this menu.
The System routines
Apart from the visual aspects, the System ROM provides software routines to operate the hardware. This includes:
- Reading button presses from the controllers and, in the case of the MVS, the coin slots.
- Accessing the Memory Card.
- Initialising VRAM with the proper structure for the sprite blocks and the Fix tile map.
Interestingly enough, system routines may, in turn, call game routines to continue some operations. This means games are also tasked with implementing certain calls [26] [27]. For instance, the System ROM may request the following from games:
- Show the custom Eyecatcher animation (if the required flag is set).
- Show the game’s boot animation.
- Start the game demo. This is what you see before inserting a coin.
- Play the ‘coin inserted’ sound.
- Begin the game after enough coins are inserted.
As you can see, most of the low-end I/O is delegated to the System ROM; games instead focus on providing their unique content.
Games
To start with, games are written in 68k and Z80 assembly. It is only with the next generation of consoles (and the arrival of new CPUs) that programming languages become part of the toolbox.
Distribution medium
Following the trend of the 4th generation, the Neo Geo relies on cartridges as its sole medium for games.
Nevertheless, I must say, Neo Geo cartridges are the largest I have seen for a home console. This is due to the amount of dedicated chips housed within. Unlike the Super Nintendo, whose games could optionally expand the capabilities of the console, Neo Geo games are strictly required to bundle a considerable amount of circuitry.

I have already mentioned some parts of the cartridge system in previous sections, but let me give you a quick summary so you get a proper overview of how this system works.
As you may know, Neo Geo cartridges are made up of two boards. The first is called PROG Board and houses the following ROM chips:
- P ROM: Stores the program the 68000 executes. It is connected with a 16-bit data bus and up to 2 MB can be addressed (more will require a mapper).
- V ROM: Stores ADPCM audio samples read by the YM2610.
By contrast, the second board is the aforementioned CHA Board and embeds the following:
- The C ROMs and S ROM. These store sprite tiles and Fix tiles, respectively.
- An M1 ROM: Stores the Z80 program. As you may know, the addressing capabilities of the Z80 are very limited (in this case, the ceiling is 62 KB). So, M1 ROM access is interfaced by a dedicated mapper called NEO-ZMC (found in the cartridge), which enables up to 512 KB of memory to be addressed. This may be expanded by adding extra mappers to the CHA Board, or by adopting the NEO-ZMC2 (which enables up to 4 MB).
Keeping progress
As a home-arcade hybrid, SNK provided a rudimentary accessory to keep track of scores and progress: a proprietary Memory Card

The Memory Card worked on both AES and MVS models. Options ranged from 2 KB to 16 KB of battery-backed SRAM [30], though in all cases the battery was unserviceable.
The save data was structured as 64 B blocks distributed across five segments, while the System ROM provided I/O routines to operate it.
Having said that, whether arcade cabinets were actually ‘prepared’ for Memory Cards… That was another story.
I knew about the Memory cards from magazines, but official Neo Geo cabinets were rare in my town. Instead, we had plenty ‘Video Sonic’ cabinets supplied by Segasa. Some lacked all the buttons required to play properly, let alone a Memory Card slot!
– Proud Neo Geo connoisseur from Jerez, Spain
Anti-piracy & Homebrew
Both consoles and games were targeted by unauthorised parties, many of whom ended up producing their own replicas [31]. Bootleg hardware was made using a combination of off-the-shelf and reverse-engineered chips, aiming to offer a cheaper alternative to SNK’s hardware.
Thus, on one side, you’ve got SNK trying to fend off bootleggers. On the other, game studios were enforcing that their code only ran on a genuine console and cartridge.
Combating fake consoles
Neither SNK nor game studios favoured running on bootleg hardware (whether it was a Neo Geo clone or a bootleg cartridge). Hence, many games bundled routines that fiddled with very particular areas of the motherboard (e.g., status flags, the real-time clock, the Watchdog, etc.) in an attempt to spot any defects in clone boards [32]. Whenever any of these checks failed, the game would display a warning message and refuse to proceed.
Fighting fake cartridges
Considering cartridges housed an exceptional number of integrated circuits, games implemented creative measures to combat piracy.
Starting with the common techniques, the System ROM contains a portion of data called Security Code that is compared side by side with the cartridge’s P ROM during boot [33]. The bootloader will proceed only if both areas match.
Additionally, games like Fatal Fury 2 also interact with their companion ‘PRO-CT0’ chip (a multiplexer for the CHA Board) to ensure the program is residing in an official cartridge [34]. Otherwise, it assumes it has been cloned, triggering many anti-piracy unpleasantries (such as making the opponent invincible).
Later on, newer entries also stored encrypted data in the C ROM, designed to be seamlessly decrypted by the ‘NEO-CMC’ (found on the CHA Board) [35]. This chip contained a set of unusual XOR functions to deobfuscate the graphics data before it reached the VDC [36]. The NEO-CMC also acts as a multiplexer for tile data within the C ROMs, allowing manufacturers to omit the inclusion of S ROM chips altogether.
For more extreme measures, games like ‘Metal Slug X’ bundled specialised ICs in their PROG board, which complicated matters further [37]. This is reminiscent of Nintendo’s CIC system, which required constant game-chip communication (albeit significantly distinct in terms of goals and architecture).
All in all, this shows that the anti-piracy battle was just another cat-and-mouse game. However, in this case, SNK was trying to steer both home and arcade owners away from cheaper knock-offs.
Post-market utilities
Once the lifecycle of this console had reached an end, a new phase emerged: Homebrew (running homemade software and/or hardware). At the time of writing (June 2024), the most common practices are hardware modifications, firmware replacement and flashcarts.
Thanks to its enthusiastic community, there are many online resources available that teach how to correct and/or modify MVS and AES hardware. These include converting MVS models to work outside cabinets (the so-called consolisation), while others focus on addressing deficiencies in particular models. For instance, the AES model I own had its video encoder bypassed, improving the quality of the RGB output.
On the firmware side, there have been developments like the ‘UNIVERSE BIOS’/UniBIOS. This is the equivalent of a custom firmware made to replace the original System ROM. Behind the scenes, the UniBIOS is made of an MVS System ROM modified to provide the following additional abilities [38]:
- Switch between ‘MVS’ and ‘AES’ mode. This is very useful for AES systems, as games have a hardcoded number of coins/lives, and switching to MVS mode enables to increase this amount arbitrarily.
- Change the region. Some games are censored depending on the region they run on.
- Activate cheats.
Finally, to run arbitrary code in this console, stores are selling third-party flashcarts which can reprogram itself to replicate any past CHA and PROG boards. Due to their complexity, they are not exactly affordable, but that is another product Neo Geo owners have available nowadays.
That’s all folks
Curiously enough, the last Neo Geo game was released in 2004, almost 14 years after its release. That’s quite an achievement for a household/arcade console, and I hope that this analysis has helped you understand these outcomes from a technical perspective.
From my side, I found it engaging to return to a 2D console after typing so many words for the Nintendo 3DS article, this helped me revisit the ‘classic’ writing structure that I adopted during the website’s beginnings in 2019.
Thinking about the follow-up articles, I’ve still got two avenues to explore: Continue the modern hardware timeline after the Nintendo 3DS, or proceed with another 2D console: The Pippin. The latter would help me introduce the PowerPC CPU, while modern hardware would enable me to talk about the ARMv7 and the ARMv8. We’ll see!
Until next time!
Rodrigo


